 |
 |
- Search
| Anesth Pain Med > Volume 15(3); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
Lidocaine is an effective against certain types of neuropathic pain. This study aimed to investigate whether timing of initiating continuous epidural infusion of lidocaine affected the glial activation and development of neuropathic pain induced by L5/6 spinal nerve ligation (SNL) in rats.
Methods
Following L5/6 SNL, rats were epidurally infused 2% lidocaine (drug infusion initiated on days 1, and 7 post SNL model establishment) or saline (saline infusion initiated on day 1 post SNL model establishment) continuously for 14 days. Mechanical allodynia of the hind paw to von Frey filament stimuli was determined prior to surgery, postoperative day 3, and once weekly after SNL model establishment. At 7 days after the infusion of saline or lidocaine ended, spinal activation of proinflammatory cytokines and astrocytes was evaluated immunohistochemically, using antibodies to interleukin-6 (IL-6) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP).
Results
Continuous epidural administration of 2% lidocaine for 14 days increased the mechanical withdrawal threshold regardless of the difference in timing of initiating lidocaine administration. Epidurally infusing 2% lidocaine inhibited nerve ligation-induced IL-6 and GFAP activation. In the 2% lidocaine infusion group, rats maintained the increased mechanical withdrawal threshold even at 7 days after the discontinuation of 2% lidocaine infusion.
Treatments of neuropathic disorders are challenging owing to their varied symptoms and multifaceted pathophysiology [1]. To date, neuropathic pain is difficult to treat and no sufficient treatment available. Instead, clinical interventions are often empirically applied to counter different symptoms as they arise. In such situations, one available option for managing neuropathic pain is continuous infusion of local anesthetics. Continuous neural blockage using local anesthetics may be promising when initial treatment is ineffective [2]. Local anesthetics, such as lidocaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine, are widely used for chronic pain and neuropathic pain [1,3]. However, owing to their relatively short duration of action, blocking must be repeated frequently to break the pain cycle. An alternative to repeated injections is continuous infusion of local anesthetics for neural blockage. This continuous infusion can exert a therapeutic effect with potent analgesic effect.
Among the continuous administration methods, intrathecal infusion methods have been extensively studied in animals to evaluate their potential therapeutic efficacies and to elucidate the underlying mechanism in a rat pain model; however, only very few studies have been conducted using continuous epidural infusion [4-6]. However, instead of intrathecal infusion, continuous epidural infusion is preferred for a variety of reasons, such as consideration of drug infusion period, and side effects, for the management of neuropathic pain in clinical settings. Therefore, the present study was conducted using continuous epidural infusion.
The L5/6 spinal nerve ligation (SNL) rat model is a classical model of nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. This model represents human-like neuropathic pain [6-8]. It was thus selected for use in this study. Previous studies have reported that if pathological activity following injury is blocked by local anesthetics, allodynia may not develop [9-11]. Using local anesthetics following nerve damage can be considered a treatment strategy for such pain. Lidocaine was selected for use as the local anesthetic as it inhibits voltage-sensitive sodium channels; sodium channel blockers have been shown to be effective in the treatment of neuropathic pain [12]. Long-term infusion of lidocaine can result in an antinociceptive effect [3].
Neuron and glial cells contribute to the initiation and maintenance of neuropathic pain [13,14]. Damage to the tissue or the nerve causes changes in glial cells [13,14]. Subsequently, these reactive spinal glial cells release cytokines and chemokines associated with hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia, contributing to neuroinflammation and central mechanisms of pathological pain [15]. Activation of spinal glial cells (astrocyte and microglia) has been demonstrated in a rat model and in patients with neuropathic disorders. Furthermore, Del Valle et al. [16] reported that spinal astrocyte and microglia were activated in a patient with neuropathic pain. Activation of glial cell because of nerve injury increased the level of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, a reactive astrocyte biomarker) and proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin 6 (IL-6) [17-19]. GFAP is known to contribute to central sensitization during neuropathic pain [18]. Expression level of IL-6 is frequently used as a marker of glial cell activation, which can occur following nerve injury or inflammation [15,17]. The suppression of microglial and astrocytic activation attenuates the development of nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain [13]. Therefore, we measured the levels of GFAP and IL-6 to determine whether continuous epidural infusion of lidocaine attenuates glial cell activation.
Although conventional animal and human studies support the use of local anesthetics for the treatment of neuropathic pain, the effects of continuous epidural infusion of local anesthetics on the progression of neuropathic pain has not yet been examined. In general, early initiation of treatment is associated with a better prognosis in neuropathic disorders [1]. However, the relationship between timing of treatment initiation and therapeutic effects has not been adequately studied. Moreover, most therapeutic drugs used in animal models of neuropathic pain were tested for a short period of 1 week. Hence, its role in the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain during a 2-week period is unclear.
Thus, we investigated whether the timing of initiating continuous epidural infusion of lidocaine for 2 weeks affected the glial activation and development of neuropathic pain induced by L5/6 SNL in rats. Also we investigated whether therapeutic effect of lidocaine maintained at 7 days after the discontinuation of 2% lidocaine infusion.
This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals of the National Research Council and the ethical guidelines for animal research by Kangwon National University. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, South Korea (no. KIACUC-17-113).
All experiments were performed with male Sprague-Dawley rats (Central Lab. Animal Inc., Korea), each weighing 200-250 g on the day of surgery. Following their arrival, rats were acclimated in their assigned cages for 2-3 days prior to experiment initiation. Rats were housed in plastic cages with soft bedding in an environment maintained at a constant temperature of 22-24┬░C in a 12-h light/dark cycle. After surgery, rats were housed in individual cages and were provided water and food ad libitum. A total of 32 male rats were randomly divided into four groups: sham (sham operation only without SNL; n = 8), control (SNL, saline infusion started 1 day after SNL model establishment and administered for 14 days; n = 8), no delay group (SNL, 2% lidocaine infusion started 1 day after SNL model establishment and administered for 14 days; n = 8), and 1-week delay group (SNL, 2% lidocaine infusion started 14 days after SNL model establishment and administered for 14 days; n = 8) (Fig. 1). The primary outcome was the change in mechanical withdrawal thresholds. Measures were taken to minimize the number of animals used in this study. The behavioral analyst was blinded to the experimental group of each animal tested. Animals that showed neurologic deficits, disability of movement after surgery, and malfunction of catheter were excluded from the study.
Rats were anesthetized with a combination of ketamine (50 mg/ml, Yuhan, Korea) and xylazine (10 mg/ml, Bayer, Germany), which was intraperitoneally administered at a dosage of 1 ml/kg. Adequate anesthesia was ascertained by the lack of ocular reflex and absence of a withdrawal response to a pinch at the hind limb. Neuropathic pain was induced following the methods of Kim and Chung [7].
Rats were anesthetized and placed under a microsurgical apparatus in the prone position. A midline incision was made on the back, and the left paraspinal muscles were separated from the spinous processes at the L4-S2 levels. The L5 transverse process was carefully removed, and the L4-L5 spinal nerves were identified. The nerves were gently separated, and the L5 nerve was tightly ligated with a 6-0 silk thread. The left L6 spinal nerve was located caudal and medial to the sacroiliac junction and then tightly ligated with a silk thread. For epidural administration of drug, polyethylene catheter (SP-45; sterile saline-filled tube; inner diameter, 0.58 mm; outer diameter, 0.96 mm; Nazme Corporation, Japan) was inserted into the epidural space through an incision in the atlanto-occipital membrane from the cervical to lumbar epidural space. The internal tip of the polyethylene tube was located close to the L3-4 level. We confirmed in preliminary experiments, using injection of a dye through the catheter, that the dye was delivered to the epidural space around the L3-L5 level in rats. Rats showing sensory dysfunction after epidurally injecting 2% lidocaine were considered to have had a successful implantation of the epidural catheter. The doses selected for epidural lidocaine infusion were based on a preliminary study, in which rats were epidurally injected 2% lidocaine and showed sensory block without blocking motor function, demonstrating normal walk during the lidocaine infusion period. After rats were euthanized, we confirmed that the tip of the catheter was appropriately located in proximity to the L3-4 level in the epidural space. The external end of the polyethylene tube was connected to a mini-osmotic pump (Alzet Model 2ML1, pumping rate 10 ┬Ąl/h, fill volume 2 ml, Durect Corporation, USA). The pump was subcutaneously fixed, and the wound was closed with silk sutures. In the control group, epidural administration of saline was initiated 1 day after SNL model establishment using the von Frey test.
The previous study reported that the longer length of epidural infusion of local anesthetics for neuropathic pain was associated with a higher success rate [2]. Considering the life cycle of the rat, 2 weeks is considered to be a sufficiently long time as the administration period of lidocaine. So we chose 2 weeks for infusion period. In previous studies using rats, the duration of continuous infusion was 1-2 weeks [4,6], so the interval of 1 week was selected as the comparison period of the therapeutic effect. In the lidocaine infusion groups, epidural administration of 2% lidocaine was initiated 1 or 7 days after SNL model was established using the von Frey test. The drug administrated continuously at a rate of 2 ml/7 days (20 mg/ml of lidocaine) for 14 days. Epidural catheter removed 7 days after the termination of drug infusion. Postoperative analgesia was not provided owing to the confounding effect of analgesics on the assessment of neuropathic pain behaviors.
An experimenter who was blinded to the group assignment performed the behavioral test. Motor function was evaluated by testing the ratŌĆÖs ability to ambulate in a normal posture and observing the righting and placing/stepping reflexes before the daily behavior assessments. To quantify mechanical allodynia, paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) of rats was determined by the von Frey test during the daylight (between 9 a.m. and 3 p.m.) [20]. Rats were allowed to acclimatize to a transparent acrylic box installed on a wire net for 30 min before the experiment. The von Frey filament was applied to the plantar skin of the hind paw. Touch perception thresholds were measured using the up-down method with von Frey hairs. Minimum stimulus intensity was 0.4 g and maximum stimulus intensity was 15 g. Each filament was applied five times. The interval of each stimulus was 3 min, and responses to three out of five stimuli were regarded as positive. Stimulus began at 2.0 g and a total of six filaments were used via the up-down method according to the response. During the experiment, a series of von Frey filaments was applied to the plantar surface of rat hind paws. A positive response was defined as sharp withdrawal of the left hind paw or immediate flinching on removal of the filament. To confirm neurologic symptoms, the PWTs were investigated using a von Frey filament (monofilament, Stoelting Co., USA) at 7-day intervals (from before experiment to sacrifice). We assessed the PWTs up to 7 days after the termination of drug infusion (Fig. 2).
Motor function was evaluated by testing the animalŌĆÖs ability to ambulate in a normal posture and observing the righting and placing/stepping reflexes before the nociceptive behavioral assessments.
Rats were euthanized by decapitation method using a guillotine by a trained person under intraperitoneal injection of ketamine (50 mg/ml) and xylazine (10 mg/ml), which was intraperitoneally administered at a dosage of 1 ml/kg, at 7 days after discontinuation of lidocaine or saline infusion.
Fluorescent immunohistochemistry was prepared to examine the change in rat spinal cord cells at 7 days after discontinuation of lidocaine infusion or at 4 weeks after the control surgery. After deep anesthesia by intraperitoneal injection of ketamine and xylazine, rats were perfused intracardially with normal saline followed by 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer (0.08 M K2HPO4, 0.02 M NaH2PO4, pH 7.4) for 20 min. The lumbar enlargement of the spinal cord was removed and fixed in 10% formaldehyde. Transverse sections of this enlargement were embedded in paraffin, sectioned (6 ┬Ąm), and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for examination under a light microscope. The hematoxylin and eosin staining procedures of Chu et al. [4] were followed. Histopathological changes were evaluated in a blinded fashion by the senior pathologist.
The ipsilateral L4-5 spinal nerve samples were removed, homogenized and centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 15 min at room temperature (23-25Ōäā). Levels of GFAP and IL-6 were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits (Wuhan fine Biological Technology Co., Ltd., China) according to the manufacturerŌĆÖs instructions. Samples were measured in duplicate, and content of each experimental sample was obtained using a standard curve.
Data are presented as median and inter-quartile range (IQR). The Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the data of experimental groups. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare the data of intra-group.
The sample size was calculated based on a previous study [10]. Considering a two-sided significance level of 0.05, 80% power, and an effect size of 0.5, power analysis estimated a needed sample size of 6 animals per group assuming a relevant effect level of 30% pain related behavior. Further, with a dropout rate of 20%, 8 animals per group (total 32 rats) were considered as ideal. For all comparisons; P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 24.0 (IBM Co., USA).
Fig. 3 shows the time course changes in right hind PWT to von Frey filaments SNL. In rats undergoing nerve ligation with saline infusion, the baseline withdrawal thresholds decreased after nerve ligation. Withdrawal thresholds did not change in rats undergoing sham operation. During the infusion period, PWTs of the 2% lidocaine infusion group significantly differed from control group (P < 0.05). In contrast, there was no significant change in withdrawal thresholds among the groups that received 2% lidocaine infusion after nerve ligation. In addition, we sought to assess neuropathic behavior at 7 days after the termination of 2% lidocaine infusion. In all groups that received 2% lidocaine infusion, rats maintained the increased mechanical withdrawal threshold even 7 days after discontinuation of 2% lidocaine infusion. No motor weakness was observed in any groups during the study period, as revealed by the normal righting/stepping reflexes and ambulation.
Fig. 4 shows the hematoxylin and eosin-stained lumbar spinal cord sections from rats receiving saline (sham group-Fig. 4A and control group-Fig. 4B) or 2% lidocaine for 14 days (no delay group-Fig. 4C and 1-week delay group-Fig. 4D). Continuous infusion of 2% lidocaine induced no obvious histopathological change in the spinal cord.
As shown in Fig. 5, continuous infusion of 2% lidocaine via an epidural catheter significantly decreased the levels of IL-6 and GFAP relative to those in the control group, regardless of lidocaine infusion time in the L4-5 spinal nerve (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in IL-6 or GFAP among the groups administered 2% lidocaine infusion at different time points. Continuous epidural infusion of 2% lidocaine was found to alleviate the production of proinflammatory cytokines in the spinal nerve of rats with SNL, indicating that it exerted an anti-neuroinflammatory effect.
In the present study, continuous epidural administration of 2% lidocaine for 14 days prevented nerve-ligation induced pain. To add, this administration for 14 days post-SNL ameliorated the development of mechanical allodynia regardless of infusion start time. Moreover, the increase in mechanical pain thresholds was maintained, even 7 days after the discontinuation of lidocaine infusion. Epidural lidocaine inhibited proinflammatory cytokine (IL-6) and astrocyte marker (GFAP) activation induced by nerve ligation. Our findings suggest that this administration could influence the regulation of SNL-induced pain and may be a promising therapeutic intervention for managing nerve injury-induced neuropathy regardless of the start time of treatment.
The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying neuropathic disorders that lead to neuropathic pain are complex and multifactorial, and certain aspects of its mechanisms are yet to be elucidated [1,3]. Neuropathic pain is usually refractory to treatment [1,17,18]. However, an attempt at local anesthesia during or immediately following injury has been postulated as a treatment strategy [9,10]. Clifford et al. [11] reported that preemptive local anesthetic attenuates the maintenance of mechanical allodynia in a rat SNL model. Thus suggesting that locally administering anesthetics, such as lidocaine, bupivacaine, and ropivacaine, close to the time of injury, reduces the development of neuropathic pain [3,10]. Administration of local anesthetics, sodium channel blocker, has attenuated ectopic discharges and suppressed the expression of the neuronal pain marker [10]. Systemic and epidural administration of local anesthetics produce analgesia and anti-hyperalgesia at doses below those that block motor nerve [5,21].
The SNL model is a notable and currently used model that reflects the mechanisms of neuropathic disorders [4-7]. The expressions of proinflammatory cytokine genes is associated with hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia [14]. Reportedly, the levels of proinflammatory cytokines are enhanced in patients with neuropathic pain syndrome, thereby implicating the influence of glia-related neuro-inflammation in its pathophysiology [16,22]. Astrocytic activity contributes to the maintenance of pain [13]. GFAP (reactive astrocyte biomarker) plays an important role in Schwann cell proliferation after nerve injury [17,18]. Schwann cells produce several proinflammatory cytokines, which mediate neuropathic pain [17,18]. These proinflammatory mediators also constitute a cytokine network that results in chronic inflammation associated with neuropathic pain. It has been suggested that activated proinflammatory cytokines and astrocytes play an important role in the initiation phase of nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain [17-19,23]. Increased spinal cytokines and GFAP levels of in SNL rats indicated the occurrence of hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in the development of neuropathic pain [24-26]. Hence, in the present study, we opted to use IL-6 and GFAP as biological markers of hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia. Our results showed that the levels of IL-6 and GFAP decreased in the groups continuously administered 2% lidocaine infusion compared with those in the control group. In addition, we found that a 2-week infusion period could increase mechanical pain thresholds.
Levels of cytokines are greater in patients with neuropathic pain syndrome, and their increase gradually resolves over a period of 6 years post-injury [27,28]. Such changes in cytokines are related to the extent of mechanical hyperalgesia [29]. In a human study, a longer treatment period was associated with a higher success rate, which indicates that treatment should be continued for long enough period to break the pathological cycle maintained by the pain [2]. In a clinical situation, duration of continuous administration is greater than 14 days and epidural infusion is a frequently used method. However, in most experimental animal studies with the neuropathic pain model, the duration is 7 days and intrathecal infusion is a frequently used method. Therefore, in the present study, we opted to continue blocking for 14 days using the epidural infusion method.
In the present study, continuous epidural blocking caused good therapeutic effects, regardless of whether treatment began within week after nerve injury. This finding implies that even if the patientŌĆÖs visit is delayed, active treatment using continuous epidural infusion of 2% lidocaine could be effective if they have nerve damage, regardless of when this damage occurs. Furthermore, we believe that continuous epidural blocking could be proactively recommended for patients with neuropathy. Long-term infusion of lidocaine is often recommended for treating neuropathic pain [1,3]. The main action of lidocaine is the blockade of voltage-gated sodium channels [30]. Based on cumulative evidence, sodium channels play a role in the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain [13,30]. Perineural administrations of local anesthetics have been used to manage chronic neuropathic pain in in previous studies [2,12]. Hence, continuously administering 2% lidocaine via epidural could be useful for treating the hyperalgesia state, such as neuropathy and neuropathic pain syndrome.
Our study has several limitations. First, IL-6 and GFAP were used as proinflammatory cytokines. Further studies should include additional types of proinflammatory cytokines. Second, the present study used ketamine to induce anesthesia. However, owing to the low dosage used (once, equally for all groups), we believe that ketamine may have not affected PWTs. Nevertheless, this is the first study to investigate the effect of a 2-week continuous epidural infusion of 2% lidocaine with different initiation times of drug infusion after spinal nerve injury. The findings obtained herein indicate that continuous infusion of epidural lidocaine not only prolongs analgesic effects but also improves therapeutic effects.
In conclusion, our results suggest that continuous epidural administration of lidocaine may serve as a promising therapeutic intervention for preventing neuropathy, not only immediately after the occurrence of neuropathic pain but also after a slight time delay.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by grant no. KSA-2020-01 from the Korean Society of Anesthesiologists.
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualizations: Yuseon Cheong, Byeongmun Hwang. Data curation: Namyoong Kim, Byeongmun Hwang. Formal analysis: Minsoo Kim. Investigation: Byeongmun Hwang. Funding: Byeongmun Hwang. Supervision: Byeongmun Hwang. Writing - original draft: Yuseon Cheong, Minsoo Kim, Byeongmun Hwang. Writing - review & editing: Byeongmun Hwang.
Fig.┬Ā2.
Timeline of control group (A), no delay group (B), and 1-week delay group (C). Bar below the X-axis represents epidural infusion with lidocaine or saline for 14 days. SNL: spinal nerve ligation, IL: interleukin, GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein.

Fig.┬Ā3.
Effect of continuous epidural infusion of 2% lidocaine for 14 days on SNL-induced mechanical allodynia, measured as paw withdrawal threshold to von Frey filament stimulus. Rats were randomly divided into four groups: sham (sham operation only without SNL), control (SNL, 2 ml/7 days, saline infusion started 1 day after SNL model establishment and administered for 14 days), no delay group (SNL, 2 ml/7 days, started 2% lidocaine infusion 1 day after SNL model establishment and administered for 14 days), and 1-week delay group (SNL, 2 ml/7 days, 2% lidocaine infusion started 7 days after SNL model establishment and administered for 14 days). Arrow indicates start point of lidocaine infusion. Values are presented as median (1Q, 3Q). SNL: spinal nerve ligation. *P < 0.05 vs. sham group. ŌĆĀP < 0.05 vs. control group (Mann-Whitney U test, n = 6-8 per group). ŌĆĪP < 0.05 vs. value just before lidocaine infusion (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, n = 6-8 per group).

Fig.┬Ā4.
Photo-micrographic representation of hematoxylin and eosin-stained lumbar spinal nerve sections from sham (A), control group (B), no delay group (C), and 1-week delay group (D). Rats received infusion of saline or 2% lidocaine (10 ╬╝l/h) for 14 days. Original magnification ├Ś 400. Spinal sections displayed normal histological appearance. Based on microscopic examination, we found no gliosis, demyelination, fibrosis, inflammation, hemorrhage, or necrosis at the lumbar level in the spinal nerve.
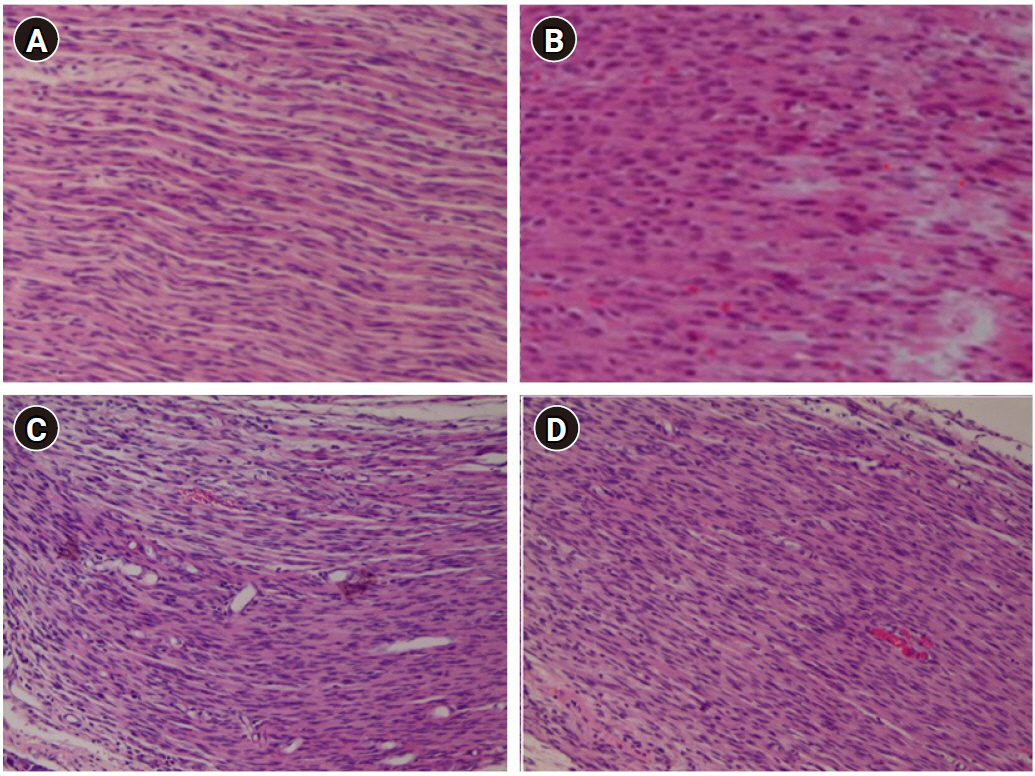
Fig.┬Ā5.
Effect of continuous epidural infusion of 2% lidocaine on the protein expressions of IL-6 (A) and GFAP (B) in a rat model of SNL-induced neuropathic pain. Rats were randomly divided into three groups: control (SNL, 2 ml/7 days, started saline infusion 1 day after SNL model establishment and administered for 14 days), no delay group (SNL, 2 ml/7 days, 2% lidocaine infusion started 1 day after SNL model establishment and administered for 14 days), and 1-week delay group (SNL, 2 ml/7 days, 2% lidocaine infusion started 7 days after SNL model establishment and administered for 14 days). Data are presented as mean ┬▒ SD. SNL: spinal nerve ligation, IL: interleukin, GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein. *P < 0.05 vs. control group.

REFERENCES
1. Harden RN, Oaklander AL, Burton AW, Perez RS, Richardson K, Swan M, et al. Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome Association. Complex regional pain syndrome: practical diagnostic and treatment guidelines, 4th edition. Pain Med 2013; 14: 180-229.



2. Moufawad S, Malak O, Mekhail NA. Epidural infusion of opiates and local anesthetics for complex regional pain syndrome. Pain Pract 2002; 2: 81-6.




3. Werdehausen R, Mittnacht S, Bee LA, Minett MS, Armbruster A, Bauer I, et al. The lidocaine metabolite N-ethylglycine has antinociceptive effects in experimental inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 2015; 156: 1647-59.


4. Chu LC, Tsaur ML, Lin CS, Hung YC, Wang TY, Chen CC, et al. Chronic intrathecal infusion of gabapentin prevents nerve ligation-induced pain in rats. Br J Anaesth 2011; 106: 699-705.


5. Li TF, Fan H, Wang YX. Epidural sustained release ropivacaine prolongs anti-allodynia and anti-hyperalgesia in developing and established neuropathic pain. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0117321.



6. Hermanns H, Muth-Selbach U, Krug S, Williams R, Braun S, Werdehausen R, et al. Effect of continuous posttraumatic intrathecal nocistatin on the development of mechanical allodynia. Reg Anesth Pain Med 2011; 36: 32-5.



7. Kim SH, Chung JM. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 1992; 50: 355-63.


8. Kim Y, Kwon SY, Jung HS, Park YJ, Kim YS, In JH, et al. Amitriptyline inhibits the MAPK/ERK and CREB pathways and proinflammatory cytokines through A3AR activation in rat neuropathic pain models. Korean J Anesthesiol 2019; 72: 60-7.



9. Xie W, Strong JA, Meij JT, Zhang JM, Yu L. Neuropathic pain: early spontaneous afferent activity is the trigger. Pain 2005; 116: 243-56.

10. Lin SC, Yeh JH, Chen CL, Chou SH, Tsai YJ. Effects of local lidocaine treatment before and after median nerve injury on mechanical hypersensitivity and microglia activation in rat cuneate nucleus. Eur J Pain 2011; 15: 359-67.


11. Clifford JL, Mares A, Hansen J, Averitt DL. Preemptive perineural bupivacaine attenuates the maintenance of mechanical and cold allodynia in a rat spinal nerve ligation model. BMC Anesthesiol 2015; 15: 135.



12. Amir R, Argoff CE, Bennett GJ, Cummins TR, Durieux ME, Gerner P, et al. The role of sodium channels in chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain. J Pain 2006; 7(5 Suppl 3): S1-29.


13. Leinders M, Knaepen L, De Kock M, Sommer C, Hermans E, Deumens R. Up-regulation of spinal microglial Iba-1 expression persists after resolution of neuropathic pain hypersensitivity. Neurosci Lett 2013; 554: 146-50.


14. Marchand F, Perretti M, McMahon SB. Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2005; 6: 521-32.


15. Cao H, Zhang YQ. Spinal glial activation contributes to pathological pain states. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2008; 32: 972-83.


16. Del Valle L, Schwartzman RJ, Alexander G. Spinal cord histopathological alterations in a patient with longstanding complex regional pain syndrome. Brain Behav Immun 2009; 23: 85-91.


17. Moalem G, Tracey DJ. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms in neuropathic pain. Brain Res Rev 2006; 51: 240-64.


18. Triolo D, Dina G, Lorenzetti I, Malaguti M, Morana P, Del Carro U, et al. Loss of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) impairs Schwann cell proliferation and delays nerve regeneration after damage. J Cell Sci 2006; 119(Pt 19): 3981-93.



19. Kiguchi N, Maeda T, Kobayashi Y, Fukazawa Y, Kishioka S. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in sciatic nerve contributes to neuropathic pain after partial sciatic nerve ligation in mice. Anesth Analg 2009; 109: 1305-11.



20. Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 1994; 53: 55-63.


21. Smith LJ, Shih A, Miletic G, Miletic V. Continual systemic infusion of lidocaine provides analgesia in an animal model of neuropathic pain. Pain 2002; 97: 267-73.


22. Alexander GM, Perreault MJ, Reichenberger ER, Schwartzman RJ. Changes in immune and glial markers in the CSF of patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Brain Behav Immun 2007; 21: 668-76.


23. Gosselin RD, Suter MR, Ji RR, Decosterd I. Glial cells and chronic pain. Neuroscientist 2010; 16: 519-31.



24. Inoue K. The function of microglia through purinergic receptors: neuropathic pain and cytokine release. Pharmacol Ther 2006; 109: 210-26.


25. Hinojosa AE, Caso JR, Garc├Ła-Bueno B, Leza JC, Madrigal JL. Dual effects of noradrenaline on astroglial production of chemokines and pro-inflammatory mediators. J Neuroinflammation 2013; 10: 81.




26. Kawasaki Y, Zhang L, Cheng JK, Ji RR. Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 5189-94.



27. Bruehl S. An update on the pathophysiology of complex regional pain syndrome. Anesthesiology 2010; 113: 713-25.


28. Wesseldijk F, Huygen FJ, Heijmans-Antonissen C, Niehof SP, Zijlstra FJ. Six years follow-up of the levels of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in patients with complex regional pain syndrome type 1. Mediators Inflamm 2008; 2008: 469439.


-
METRICS

-
- 2 Crossref
- 5,426 View
- 88 Download
- Related articles in Anesth Pain Med
- ARTICLE & TOPICS
-
- Topics
-
- Neuroscience in anesthesiology and critical care
- Anesthetic Pharmacology
- Obstetric Anesthesia
- Pediatric Anesthesia
- Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia
- Transplantation Anesthesia
- Spinal Pain
- Regional Anesthesia
- Neuromuscular Physiology and Pharmacology
- Airway Management
- Geriatric anesthesia and Pain
- Others