Considerations regarding anesthesia for renal transplantation
Article information
Abstract
Renal transplantation is a complex surgical procedure requiring meticulous anesthetic planning to ensure patient safety and optimal graft function. In this comprehensive review, we examined various aspects of anesthesia management during renal transplantation, including preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care. Preoperative optimization involves the identification and management of risks to mitigate perioperative complications. Treatment with erythropoiesis-stimulating agents is recommended to correct anemia in transplant recipients with hemoglobin levels below 9-10 g/dl. Intraoperative management focuses on hemodynamic monitoring, maintenance of intravascular volume, and careful selection of anesthetic techniques. Neuromuscular monitoring and the appropriate use of neuromuscular blocking and reversal agents are considered essential. Further, hemodynamic goals include maintaining the mean arterial pressure within the range of 80-110 mmHg. In addition, attention should be paid to perioperative glycemic control, temperature management, and diuretic use. In postoperative management, multimodal analgesia and the prevention of postoperative delirium contribute to optimal recovery. The implementation of enhanced recovery after surgery principles can further improve outcomes. Collaborative efforts among surgical teams, anesthesiologists, and healthcare professionals are crucial for achieving successful renal transplantation outcomes.
INTRODUCTION
Renal transplantation is the most common surgery for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) caused by a variety of different conditions. The first successful renal transplantation was reported in 1954 [1]. In more recent years, the one-year survival rates of deceased-donor grafts in the United States, Europe, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand have consistently exceeded 90% [2]. Living donor renal transplantation is widely performed in many African and Asian countries, whereas deceased donor renal transplantation is predominantly performed in some European countries [3].
The history of renal transplantation in South Korea began with the first living donor transplantation in 1969 and the first deceased donor transplantation in 1979 [4]. In 2021, 2,227 renal transplantations were performed in South Korea, with a one-year survival rate of 95.9% for deceased donors and 98.8% for living donor transplants [5].
Renal transplantation is recommended for patients with ESRD due to various underlying conditions. In the United States, the most prevalent indication for renal transplantation is nephropathy associated with hypertension and diabetes [6]. Renal transplantation is a highly complex surgical procedure that requires intricate anesthetic planning to ensure patient safety and optimal functioning of the transplanted kidneys. Herein, we aimed to comprehensively review considerations related to anesthesia in renal transplantation surgery.
PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
Preoperative optimization
Preoperative assessment and optimization of identified risks can be applied to mitigate perioperative risks, such as cardiovascular, pulmonary, or other medical complications. Jaszczuk et al. [7] proposed the following recommendations: (1) Patients presenting with unstable coronary syndromes, decompensated heart failure, significant valvular disease, or arrhythmias should undergo reevaluation of their cardiac status. (2) Echocardiography should be performed in individuals with impaired ventricular function, valvular abnormalities, or a risk of developing pulmonary hypertension. (3) Cardiologist assessment is necessary for recipients with pulmonary systolic pressure exceeding 45 mmHg, and symptomatic patients should undergo pulmonary function testing. (4) Patients should cease smoking for a minimum of four weeks prior to surgery, and nicotine replacement therapy should therefore be offered to smokers. (5) Preoperative screening for frailty should be conducted to assess the patient risk.
Preoperative anemia correction
Anemia is prevalent among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), with higher rates in patients with stage 5 CKD [8]. Adverse outcomes, including increased mortality, infection, and iron overload, are all associated with blood transfusion [9]. Avoiding transfusions is recommended for potential kidney transplant recipients [10]. The consideration of erythropoiesis-stimulating agent treatment is recommended for renal transplantation recipients with hemoglobin levels < 9-10 g/dl [7].
INTRAOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
Intraoperative hemodynamic monitoring
The primary objectives of intraoperative monitoring are to ensure adequate renal blood flow to the renal graft and maintain optimal intravascular volume status. The basic noninvasive monitoring methods include noninvasive blood pressure monitoring, electrocardiography, pulse oximetry [11]. Capnography, urine output monitoring, and temperature monitoring have also been implemented [11].
Owing to the high prevalence of significant cardiac comorbidities among patients, as well as the potential for recipients to become unstable during the intraoperative period, the use of a central venous catheter is recommended [12]. In the presence of a central venous catheter, it is possible to administer vasoactive drugs and monitor central venous pressure. However, central venous pressure is not considered a reliable indicator of fluid status or responsiveness [13].
An intra-arterial catheter can be used to continuously monitor arterial blood pressure and hemodynamic parameters, such as stroke volume, stroke volume variation, and cardiac output. Additionally, it can facilitate intermittent blood sampling for point-of-care laboratory testing, including the measurement of electrolytes (potassium and sodium), arterial oxygen partial pressure, arterial oxygen saturation, arterial carbon dioxide partial pressure, and glucose and hemoglobin concentrations. In patients with advanced coronary artery disease, ventricular dysfunction, and pulmonary hypertension, the use of a pulmonary artery catheter or transesophageal echocardiographic monitoring may be considered [14]. During renal transplantation, delayed graft function can occur if the mean arterial pressure (MAP) falls below 70 mmHg. Several studies have recommended maintaining an MAP range of 80-110 mmHg [7,15].
Adequate expansion of the intravascular volume through the administration of crystalloids or colloids has been shown to increase renal blood flow, leading to improved immediate graft function [11]. To avoid hypotension, the maintenance of an appropriate intravascular volume and control of anesthetic agents are necessary. If hypotension persists despite an adequate intravascular volume, administration of small doses of vasopressors may be considered [16]. Dopamine is not recommended owing to its potentially harmful effects [17], while norepinephrine is the preferred choice [18,19].
Anesthetic technique
Patients with ESRD are known to be at an increased risk of aspiration. To reduce this risk, the administration of an oral non-particulate antacid may be considered to increase gastric pH and an intravenous H-2 blocker can be administered to decrease gastric acid secretion prior to anesthesia induction [14].
General anesthesia is the most frequently used routine technique for renal transplantation [20]. Rapid sequence induction is preferred to prevent aspiration pneumonia [14].
1. Induction of anesthesia
Propofol and thiopental are both considered safe drugs to induce general anesthesia. Ketamine should be avoided in patients with ischemic heart disease (IHD) due to its potential for sympathetic stimulation. In contrast, etomidate may be a suitable choice for patients with IHD or impaired ventricular function owing to its high cardiovascular stability [7]. Fentanyl, alfentanil, sulfentanil, and remifentanil can be safely used, whereas morphine should be avoided because of the potential for its metabolite morphino-6-glucuronide to cause end-stage renal failure [7].
2. Maintenance of anesthesia
In animal studies, sevoflurane has shown potential nephrotoxic effects linked to its metabolites, compound A, and fluoride ions. However, research conducted in humans has not provided evidence of any harmful effects on renal function [21,22]. Desflurane, isoflurane, and propofol can be used for anesthesia [7].
3. Neuromuscular blocking agents and reversal agents
Neuromuscular monitoring is recommended for patients with ESRD, especially those undergoing renal transplantation [12,23]. Succinylcholine can be administered when the serum potassium level is < 5 mEq/L [24]. The use of rocuronium and vecuronium is possible, although it may result in an increased duration of action [7]. Atracurium and cisatracurium are also used to promote organ-independent drug clearance. However, its metabolite laudanosine has the potential to induce seizures [7,14].
The clearance of the sugammadex-rocuronium complex is reduced in patients with ESRD as it is primarily eliminated through the kidneys. However, sugammadex appears to be safe and effective in renal transplant recipients [25,26].
Perioperative glycemic control and temperature management
Perioperative hyperglycemia can lead to unfavorable outcomes in both diabetic and nondiabetic patients [27]. The recommended blood glucose ranges vary slightly depending on the study, with ranges of 110-160 mg/dl [27] and 140-189 mg/dl [28,29] both being reported.
Perioperative hypothermia is associated with a variety of complications, including surgical site infection, coagulopathy, pain, prolonged response to neuromuscular blocking agents, adverse cardiac events, and longer hospital stay [30]. While research specifically on target body temperature in renal transplantation is not extensive, Jaszczuk et al. [7] recommend maintaining a minimum temperature of at least 36.5℃ during surgery and checking the patient's temperature every 30 min during surgery and every 15 min during the recovery phase.
Diuretics and albumin
Mannitol, an osmotic diuretic, is commonly administered in renal transplantation patients to induce rapid intravascular volume expansion, improve renal flow, protect against posttransplantation tubular necrosis, eliminate free radicals, and increase prostaglandin production [18,31,32]. The administration of 250 ml of 20% mannitol prior to reperfusion has been shown to enhance renal function and reduce the incidence of delayed graft function (DGF) during renal transplantation [23]. Excessive administration of mannitol can lead to adverse effects, including heart failure, pulmonary edema, and hypertonic kidney failure [31]. However, evidence supporting the efficacy of mannitol and other agents in reducing the incidence of acute tubular necrosis remains limited.
Furosemide (3-5 mg/kg) is routinely administered 10-15 min prior to clamp release during renal transplantation [7]. It exhibits nephroprotective effects by counteracting the antidiuretic hormone response and reducing renal oxygen consumption by blocking active tubular transport, which provides resistance against ischemia [24]. However, the evidence supporting the beneficial effects of furosemide in patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) is not robust [12,23]. Furthermore, there is research to indicate that low urine output following furosemide administration predicts the need for postoperative renal replacement therapy [33,34]. Finally, there is no significant advantage associated with the use of albumin compared with crystalloids in renal transplant recipients [35].
POSTOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
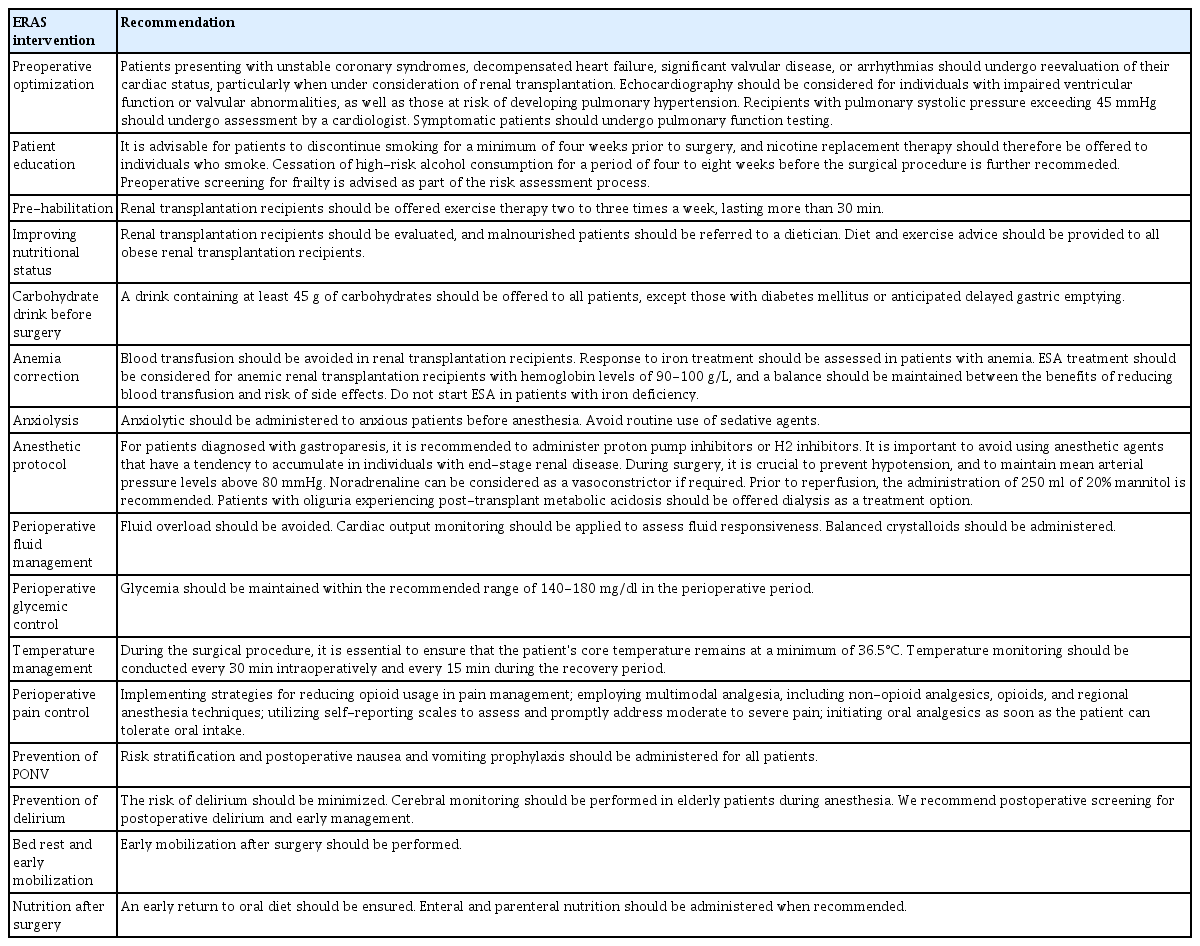
The recommendations for enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) that can be applied to renal transplantation are listed in Table 1 [10].
Perioperative pain control
Significant variations in pain after renal transplantation have been reported, with some patients experiencing severe and challenging pain management [7,14]. The pharmacokinetics of most opioid medications are altered in patients with renal failure, necessitating dose reduction. Furthermore, postoperative pain in renal transplant recipients can be influenced by pre-existing chronic pain conditions and opioid dependence, which are prevalent in 40-60% of dialysis patients [36].
According to the the ERAS guidelines, multimodal analgesia, including opioids, non-opioid analgesics, and regional anesthesia, is recommended to optimize postoperative pain control, facilitate early recovery, and expedite oral intake and mobilization. The guidelines also highlight the importance of using self-reporting scales to assess and promptly manage moderate-to-severe pain and initiating oral analgesia as soon as the patient is able to tolerate oral intake [7].
Prevention of postoperative delirium
Postoperative delirium (POD) can occur in renal transplant recipients, particularly those who are vulnerable or frail. This condition is characterized by an acute decline in cognitive function and presents with inattention, impaired consciousness, disorientation, memory impairment, hallucinations, delusions, and psychomotor disorders. POD, which can occur in up to 50% of older surgical patients, is further associated with adverse outcomes, including prolonged length of hospital stay, graft loss, and mortality. Appropriate interventions can reduce the incidence of POD by 40% [37]. To prevent POD, routine premedication with benzodiazepines and anticholinergic drugs should be avoided [7]. Non-pharmacological preventive measures, such as cognitive orientation, sensory enhancement with visual/hearing aids, noise reduction, optimizing sleep hygiene, avoiding unnecessary internal catheters, medication reviews, early mobilization, and ensuring good nutrition are all recommended [38].
Cerebral monitoring is recommended in elderly patients undergoing anesthesia. In addition, screening for POD is crucial. Early detection via screening enables prompt management and intervention [7].
CONCLUSION
Renal transplantation is not only an important surgery that saves the lives of patients, but is also important to their family members. Similar to the surgery itself, anesthesia plays a significant role in renal transplantation. As such, it is crucial for anesthesiologists to be involved in the entire process, from preoperative preparation to postoperative care. Preoperative optimization involves the identification and management of risks to reduce perioperative complications. Intraoperative management focuses on monitoring hemodynamics, maintaining intravascular volume, and carefully selecting anesthetic techniques. Neuromuscular monitoring and appropriate utilization of neuromuscular blocking and reversal agents are crucial. Hemodynamic targets include maintenance the mean arterial pressure between 80-110 mmHg. Perioperative attention is required to monitor anemia, glycemic control, temperature regulation, and diuretic use. In postoperative management, multimodal analgesia and prevention of postoperative delirium contribute to optimal recovery. Overall, optimal outcomes are achieved when surgeons, anesthesiologists, and other healthcare professionals all work together with patients.
Notes
FUNDING
None.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Writing - original draft: Hyunjee Kim, Hoon Jung. Writing - review & editing: Hyunjee Kim, Hoon Jung. Conceptualization: Hyunjee Kim, Hoon Jung. Data curation: Hoon Jung. Formal analysis: Hyunjee Kim, Hoon Jung. Methodology: Hyunjee Kim, Hoon Jung. Funding acquisition: Hyunjee Kim, Hoon Jung. Visualization: Hyunjee Kim, Hoon Jung. Investigation: Hoon Jung. Resources: Hoon Jung. Software: Hoon Jung. Supervision: Hoon Jung. Validation: Hyunjee Kim, Hoon Jung.