INTRODUCTION
Despite the many advantages of laparoscopic and robotic gynecologic surgeries, the disadvantages of elevated intracranial pressure (ICP) and intraocular pressure (IOP) remain, which are caused by the steep angle of the Trendelenburg position and the induced carbon dioxide (CO
2) pneumoperitoneum [
1,
2]. Weber et al. [
3] reported that elevated IOP causes ocular venous congestion and hypoperfusion of the optic nerve, which lead to ischemic optic neuropathy or postoperative visual loss. Monitoring the ICP during laparoscopic surgery in the Trendelenburg position is useful for the management of patients under anesthesia, as it helps to prevent neurologic complications, such as neurologic deterioration or optic neuropathy. However, direct measurement of ICP using methods such as extraventricular drainage is invasive and poses a risk of infection [
4]. Sonographically measured optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) has recently been suggested as a simple and non-invasive method for detecting increased ICP [
5,
6]. Using the changes in ONSD as an indicator for increasing ICP, several studies have shown that the patient’s position affects the ONSD in surgeries with induced CO
2 pneumoperitoneum that are performed in the Trendelenburg position [
7-
9]. Previous studies compared propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) to sevoflurane anesthesia using IOP measurement. Kaur et al. [
10] demonstrated that propofol-based TIVA was superior to sevoflurane anesthesia by direct intraoperative measurement of IOP during laparoscopic surgery in the Trendelenburg position. Yoo et al. [
11] also observed that propofol-based TIVA is superior to sevoflurane anesthesia in attenuating the increase of IOP during laparoscopic surgery in the Trendelenburg position.
On this basis, we postulated two hypotheses. First, the ONSD in patients undergoing gynecologic surgery should significantly increase during the surgery in both groups. Second, the changes in ONSD will depend on the anesthetic agents used, either sevoflurane anesthesia or propofol-based TIVA. Other possible influencing parameters that were evaluated in both groups included respiratory and hemodynamic parameters, such as heart rate, mean blood pressure, peak inspiratory pressure, and end-tidal CO2.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
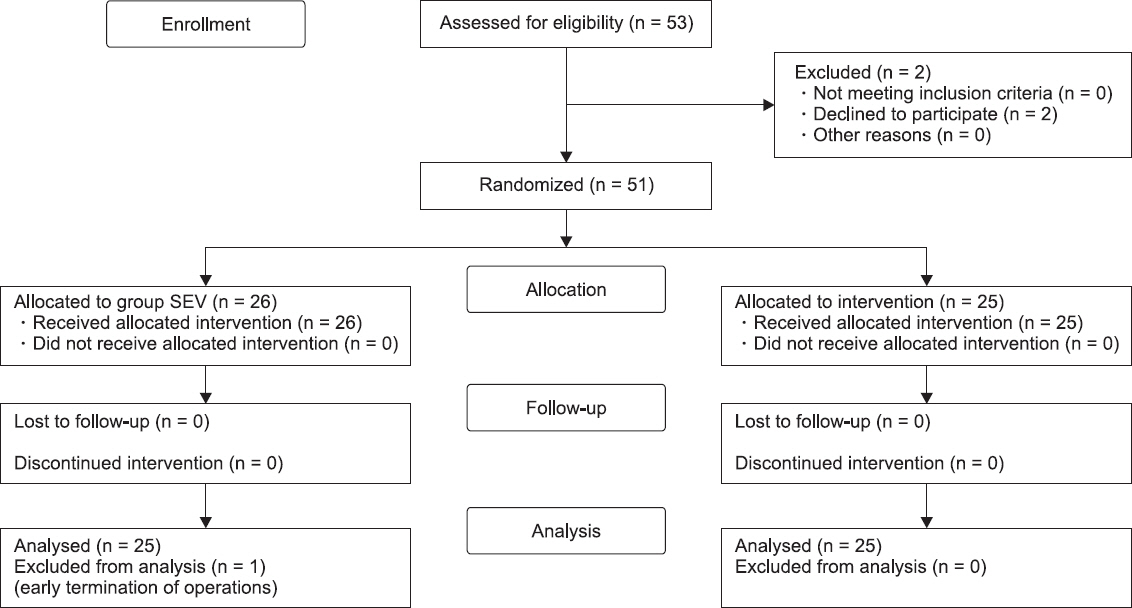
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of our hospital (no. 2018-06-007-002). The study was conducted in the Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine of the University Hospital, in the period from July 2018 to October 2018. Fifty-three female patients of American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status classes I and II, aged between 20 and 65 years, who underwent elective robotic or laparoscopic gynecologic surgery, such as robot-assisted myomectomy, robotic or laparoscopic total hysterectomy, robot-assisted sacrocolpopexy, and ovarian cystectomy, met the eligibility criteria of the study. Informed consent for participating in the study was obtained from all participants. Exclusion criteria included the following: patient refusal, history of eye disease, diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy, cataract, or glaucoma, history of allergy to anesthetic drugs, and pregnancy. A computer-generated table of random numbers was used to randomly divide the patients into two groups: patients that received inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane (group SEV, n = 25), and patients that received propofolbased TIVA (group TIVA, n = 25) (
Fig. 1).
Fig. 1
Consolidated standards of reporting trials flow diagram of the study. Group SEV: sevoflurane anesthesia, Group TIVA: propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia.
Standard anesthesia techniques were applied in all patients. After identification, the patient was connected to monitoring devices: an electrocardiograph, pulse oximetry (SpO2) monitor, non-invasive blood pressure monitor, and bispectral index (BIS) monitor (A-2000®, Aspect Medical Systems, USA). Glycopyrrolate (0.2 mg) and midazolam (3 mg) were administered before induction of anesthesia in both groups. In group SEV patients, anesthesia was induced using sevoflurane, and the end-tidal effect-site concentration (Ce) of sevoflurane was then adjusted to 2 vol%. In group TIVA patients, anesthesia was induced using propofol (2 mg/kg; Ce: 3.0 μg/ml) and remifentanil (50-100 μg; Ce: 5 ng/ml), administered by a target-concentration controlled infuser (Orchestra® Base Primea, Fresenius Vial, France). In both groups, endotracheal intubation was done within 90 s of administration of rocuronium (0.6 mg/kg, intravenous), and the patient was ventilated via a 3 L/min oxygen-air mixture (50:50), using a tidal volume of 8 ml/kg. The peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) was kept at 30 cm H2O during anesthesia. A respiratory rate of 10-12 breaths/min was set to maintain the end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) level between 35 and 40 mmHg. Anesthesia was maintained with sevoflurane (Ce: 1-3 vol%) and fentanyl (up to 100 μg) in group SEV, and propofol (Ce: 1.5-3 μg/ml)-remifentanil (Ce: 2-8 ng/ml) infusion in group TIVA, to achieve the appropriate depth of anesthesia, indicated by a BIS score of 40 to 60 and hemodynamic parameters within ± 20% of the baseline value. Rocuronium (0.2 mg/kg/h) was infused continuously for muscle relaxation during robotic surgery. Body temperature was measured using an esophageal temperature probe and was maintained at 36-37°C by a forced-air warming system.
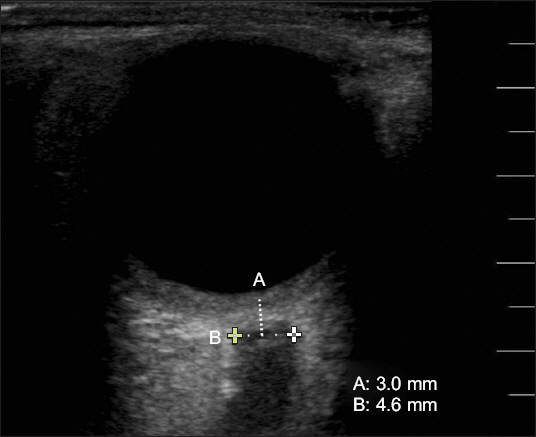
The ONSD was measured at five points (T0-T4). The baseline ONSD was measured via ultrasonography (FUJIFILM
®, Sonosite Inc., USA) in the supine position. We placed the linear probe lightly over the closed upper eyelids. The diameter of the optic nerve sheath was measured at a point 3.0 mm behind the optic disc. The ONSD appears as a vertical hypoechoic band surrounded by retrobulbar echogenic fat tissue on a monitor, perpendicular to the ultrasonic probe (
Fig. 2). Using gel, the linear probe (13-16 MHz) was gently applied—transversely at 3-5 mm—to the patient’s upper eyelids to avoid excessive pressure, by two experienced examiners (one resident and one non-resident). For the purpose of ensuring inter-observer reliability, both examiners averaged over two measurements each for the first 10 random patients in the study. The ONSD was measured twice in each eye and calculated as the average of the four values. T0 was measured 5 min after induction of anesthesia in the supine position, when vital signs were stable. The Trendelenburg positioning and CO
2 insufflation were usually done simultaneously. The intra-abdominal pressure of the CO
2 pneumoperitoneum was set as 12 mmHg, and the degree of the Trendelenburg position was set as 30-32°, slightly differing between beds. The ONSD was measured in the same way at 5, 15, and 30 min after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction in the Trendelenburg position (T1, T2, and T3 respectively). Finally, T4 was measured 5 min after the discontinuation of the CO
2 pneumoperitoneum in the supine position. In the occasions when the exsufflation time preceded the time at which the bed was made supine, we measured the ONSD after the patient was put in the supine position. The respiratory and hemodynamic parameters, such as heart rate (HR), mean blood pressure (MBP), PIP, and ETCO
2 were also recorded at each time point. Glycopyrrolate (0.4 mg) and pyridostigmine (10 mg) were administered after two further train-of-four recordings. Extubation was then carefully done after checking hand grip and head lift. Postoperatively, all patients were observed in the recovery room and in the ward on the day of surgery for confirming neurologic complications.
Fig. 2
Optic nerve sheath diameter is measured by ultrasonography. The linear probe is placed lightly over the closed upper eyelids. The diameter of the optic nerve sheath (B) is measured as 4.6 mm at a point 3.0 mm (A) behind the globe.
Statistical analysis
Previous studies suggest that the normal ONSD range is 4.6 ± 0.3 mm, with the cutoff value of > 5.0 mm for detecting ICP > 20 cm H
2O [
12]. The sample size was calculated using a twotailed test, effect size 1, significant level (α = 0.05) and 90% power; therefore, the number of each group was 23. We set the number of each group to 25, considering a 10% dropout rate. All data were analyzed statistically using the SPSS software, Version 18.0 (IBM Corporation, USA). All continuous variables are presented as mean ± standard deviation. Student’s t-test was used for the demographic variables, and chisquare test was used for the categorical variables. Repeated measures analysis of variance was used for inter-group and intra-group differences for repeated measured variables, such as ONSD, HR, MBP, PIP, and ETCO
2. Bonferroni’s test was performed for further post hoc analysis. A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
We received an informed consent from 53 patients. Three refused to participate in the study (
Fig. 1).
There were no significant differences in the demographic data between the two groups (P > 0.050): duration (min) of surgery, anesthesia, CO
2 pneumoperitoneum, Trendelenburg position, and the degree (°) of the Trendelenburg position (
Table 1).
Table 1
Demographic Variables and Duration of Surgery in Two Groups
|
Variable |
Group SEV (n = 25) |
Group TIVA (n = 25) |
|
Age (yr) |
44 ± 11.9 |
45 ± 13.8 |
|
Height (cm) |
158 ± 5.6 |
161 ± 5.7 |
|
Weight (kg) |
56 ± 9.8 |
58 ± 6.8 |
|
ASA PS classification (I/II) |
15/10 |
15/10 |
|
Past medical history |
8 |
5 |
|
Laparoscopic/robotic surgery |
6/19 |
9/16 |
|
Anesthesia time (min) |
153.6 ± 61.7 |
149.8 ± 54.9 |
|
Operation time (min) |
112.8 ± 56.2 |
104.2 ± 50.3 |
|
CO2 pneumoperitoneum time (min) |
73.5 ± 41.5 |
67.8 ± 38.5 |
|
Trendelenburg angle (°) |
31.5 ± 1.4 |
30.8 ± 1.7 |
|
Trendelenburg time (min) |
74.8 ± 39.8 |
69.0 ± 39.0 |
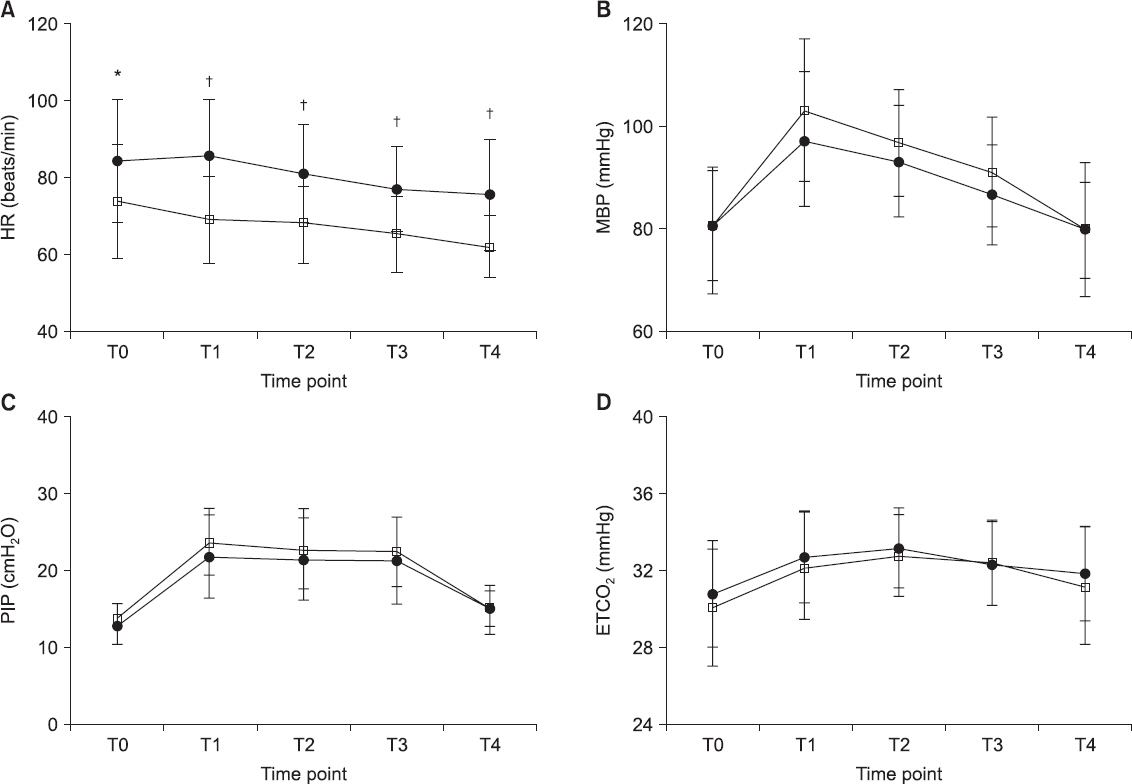
HR and MBP increased significantly 5 min after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum was induced in the Trendelenburg position (T0 vs. T1, P < 0.001,
Fig. 3). The HR in group TIVA was significantly lower than that in group SEV (T1-T4, P < 0.001,
Fig. 3), even though there were no inter-group differences in MBP (T1, P = 0.266,
Fig. 3). The PIP and ETCO
2 increased significantly after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction in the Trendelenburg position in both groups; however, there were no significant inter-group differences (T0-T4, P = 0.302 in PIP; T0-T4, P = 0.493 in ETCO
2;
Fig. 3).
Fig. 3
Trends of heart rate (A), mean arterial pressure (B), peak inspiratory pressure (C), and end-tidal carbon dioxide (CO2) (D) are shown in both groups. Group SEV (•): sevoflurane anesthesia, group TIVA (□): propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia. There are no significant differences between the two groups except in heart rate. Heart rate in group TIVA was significantly lower than that in group SEV at T1-T4. T0 = 5 min after induction of anesthesia in supine position; T1, T2, and T3 = 5, 15, and 30 min after CO2 pneumoperitoneum in the Trendelenburg position; T4 = 5 min after CO2 discontinuation in the supine position. HR: heart rate, MAP: mean arterial pressure, PIP: peak inspiratory pressure, ETCO2: end-tidal CO2. Changes in ONSD at each time point were compared using repeated measure of analysis of variance. *Indicates P < 0.050 between two groups; indicates P < 0. 001 between two groups.
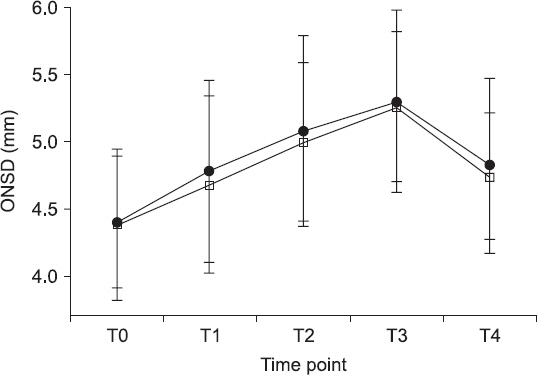
An increase in the ONSD after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction and Trendelenburg positioning was observed over time in both groups (T0 vs. T1-T3, P < 0.001,
Fig. 4). However, there were no inter-group differences in the ONSD changes (P = 0.552,
Fig. 4). The mean length of hospital stay was 2 days, and there were no registered neurologic complications in the recovery room or in-ward on the day of the surgery.
Fig. 4
Trends of optic nerve sheath diameter are investigated at different time intervals. Group SEV (•): sevoflurane anesthesia, group TIVA (□): propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia. The graph shows the mean values ± SD. There are no significant differences in ONSD between group SEV and group TIVA. The intra-group increase in ONSD over time is significant in both groups (P < 0.05). Changes in ONSD at each time point were compared using repeated measure of analysis of variance. ONSD: optic nerve sheath diameter; T0 = 5 min after induction of anesthesia in supine position; T1, T2, and T3 = 5, 15, and 30 min after CO2 pneumoperitoneum in the Trendelenburg position; T4 = 5 min after CO2 discontinuation in the supine position.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, we found that there were no significant differences in the ONSD between patients who underwent sevoflurane anesthesia and those who underwent propofol-based TIVA until 30 min after inducing CO2 pneumoperitoneum and placing the patients in Trendelenburg position during gynecologic surgery.
Previous studies suggested that measurement of the ONSD is a non-invasive, indirect method of estimating changes in ICP [
5,
6,
13]. In addition, measurement of the ONSD was considered as a screening technique for patients with increased ICP [
14]. Recently, there was controversy regarding the cutoff value of ONSD that indicates increasing ICP, which ranged from 4.85 to 5.9 mm [
15-
17]. Because researchers applied different backgrounds and settings, the cutoff value was measured differently. In the present study, we used a cutoff value of 5 mm to predict ICP greater than 20 cm H
2O as previous studies suggested, with a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 93% [
12].
Moreover, several studies have been conducted to determine the relationship between the ONSD and CO
2 pneumoperitoneum in the Trendelenburg position [
7-
9,
18]. These studies suggested that CO
2 insufflation increases cerebral blood flow and eventually ICP, because the cerebral blood flow changes at 1.8 ml/100 g/min for each 1 mmHg change in the PaCO
2 [
19]. Further, it was suggested that the same tidal volume in the Trendelenburg position, compared with the supine position, derives a higher intrathoracic pressure, which is transmitted to the intracranial space and leads to increased ICP [
7].
Recently, many researchers have been exploring the changes in IOP related to the use of different anesthetic methods. They suggested that increased IOP should be considered as decreased perfusion of the optic nerve, which may contribute to ischemic optic neuropathy [
10,
11,
20]. On this basis, we hypothesized that the ONSD, as it relates to the use of sevoflurane anesthesia versus propofol-based TIVA, is significantly different in laparoscopic and robotic gynecologic surgery performed in the Trendelenburg position. Because the optic nerve is surrounded by subarachnoid space, the ONSD increases as the ICP increases [
21].
In our results, the baseline ONSD, which was measured at 5 min after induction of anesthesia (T1), was similar in both groups: 4.38 ± 0.56 in group SEV and 4.40 ± 0.49 mm in group TIVA. After CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction and Trendelenburg positioning, the ONSD steadily increased from the baseline value in both groups, peaking at 30 min after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction and Trendelenburg positioning (T3). However, we could not find significant differences in the ONSD between the two groups until T3. In accordance with our findings, Verdonck et al. [
9] reported that the ONSD remained constant at 190 min after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction with full Trendelenburg position at 45° in robotassisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALRP). They suggested that the mechanism of a small increase in ICP in CO
2 pneumoperitoneum and a head-down position is related to the Monro-Kellie doctrine [
22]. Although the CO
2 pneumoperitoneum and head-down position lead to an increase in arterial and venous volumes, which induces increase in the ICP [
23], other brain components, such as blood, CSF, and brain parenchyma—which are surrounded by fixed intracranial volume—maintain their equilibrium state simultaneously. In other words, increase in the volume of one compartment, such as the intracranial blood volume, is compensated by decrease in the volume of others, such as the CSF [
22], and this leads to maintenance of the ICP. It seems that the similar changes in the ONSD at 30 min after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction and Trendelenburg positioning in our study can be explained by the same compensatory mechanism mentioned above.
Contrary to our findings, Yu et al. [
24] and Choi et al. [
25] showed that the ONSD was significantly lower during propofol anesthesia than during inhalation anesthesia after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction and Trendelenburg positioning in RALRP. Yu et al. [
24] reported that there are no significant differences in the ONSD between the two groups until 30 min after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction and Trendelenburg positioning, corresponding to T3 of our study. In contrast to our study, their mean anesthesia time was 189.2 ± 19.8 min, which is twice as long as ours, and the average age of their patients was 65 years, which is greater than that of ours (45 years). These two factors, anesthesia time and average age of patients, may be the cause of the differences in the results when compared with those of our study. Choi et al. [
25] also reported that the mean ONSD in a propofolbased TIVA group is significantly lower than in a desflurane group in RALRP. They showed that the effect of inhalation anesthetics on increasing cerebral blood flow is dependent on the intrinsic cerebral vasodilatory activity and cerebral vascular smooth muscle relaxation in a dose-dependent manner [
26]. In contrast, propofol constricts cerebral vascular smooth muscle, corresponding to a reduction in cerebral blood flow, which leads to a decrease in ICP [
27]. Moreover, based on a previous study, the changes in the ONSD during RALRP were related to age. The variation in the ONSD was greater in older patients than in patients aged less than 63 years [
28]. This may indicate better autoregulation of the ICP in younger patients. Therefore, the insignificant changes in the ONSD between the two groups can be attributed to the autoregulation of ICP in a young and healthy female population and to the relatively short surgery time in laparoscopic or robotic gynecologic surgeries. Further investigation is needed to evaluate the changes in the ONSD up to 60 min after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction and Trendelenburg positioning, simultaneously considering the age factor.
Our study has several limitations. Even though one resident and one non-resident examiner each measured the ONSD twice, it was difficult to ensure accuracy of the measurement because of the minute length of ONSD. Second, since our study was conducted on the basis of gynecologic surgeries of relatively short durations, we could not measure changes in the ONSD at the points of 1 or 2 h after CO
2 pneumoperitoneum induction and Trendelenburg positioning. Further analysis regarding the correlation between surgery time and changes in the ONSD in the propofol-based TIVA group is needed. Third, we only measured the ONSD when patients were under general anesthesia and excluded the data regarding the ONSD before anesthesia. Despite setting the default value as a pre-anesthetic value, we might not have gained a larger difference between the two groups. Fourth, even though we set 5 mm as the cutoff value of the ONSD associated with increasing ICP [
12], consensus regarding the optimal cutoff has not been established as it relates to the type of surgery and patient characteristics. Furthermore, because our study was conducted only in young women of American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status classes I and II, further study is necessary to explore whether the increase in the ONSD in elderly patients with pre-existing disease causes neurologic complications after surgery. Even though there were no detected neurologic complications in the recovery room or in-ward on the day of the surgery, we did not track the postoperative course, thus neurologic complications with reversible neurologic deficit, such as transient ischemic attack, may not have been detected.
There were no significant differences in the ONSD between patients undergoing sevoflurane anesthesia and those undergoing propofol-based TIVA up to 30 min after CO2 pneumoperitoneum induction and Trendelenburg positioning in gynecologic surgery. Our results suggest that there is no significant difference between sevoflurane anesthesia and propofol-based TIVA in relatively short operations.